What is Going on in Cybersecurity?
A high-level overview of cybersecurity terminology
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is part of information security, which aims to keep both physical and digital data secure, but cybersecurity only deals with digital ones. The term "cyber" is often used too broadly due to the increasingly complex nature of information in the digital age. In practice, cybersecurity addresses primarily those types of attacks, breaches, or incidents that are targeted, sophisticated, and difficult to detect or manage. The main goal of cybersecurity is to design and put effective controls in place that will help protect businesses and people from intentional attacks, breaches, incidents, and consequences.
Key cybersecurity concepts and their relationships:
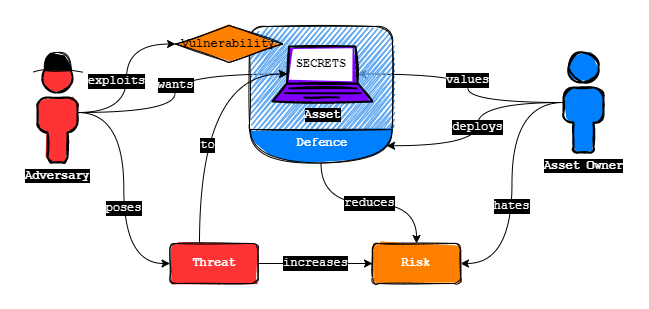
Source: Author's own
The Asset
The graph illustrates the interrelationships between various key principles. At the centre is the subject of cybersecurity, which is the value (asset or resource) that we or others, as owners or users, seek to protect. A computer system's assets are classified as follows: data, software, hardware, network, and infrastructure.
The Owner
People who rely on computer and network systems own the data that is stored or own the systems in which the data is stored. They deploy them because the systems or data are vital to their work.
Vulnerabilities
In the context of security, our concern is the vulnerabilities of the resources. The very general categories of vulnerabilities of a computer system or network asset are:
Corruption of the system might lead to incorrect behaviour or responses from the system. It's possible that, for example, data saved in a database may have been incorrectly altered (we want
integrity).Leaks can occur in the system. Someone who shouldn't have access to any or all of the network's information, for example, does so (we want
confidentiality).
- It's possible that the system will go down or be extremely slow. Because of this, it is difficult to use the system or network (we want
availability).
Threats and Attacks
Threats capable of exploiting the various sorts of vulnerabilities in a system resource correspond to those vulnerabilities. A threat is a potential security risk to an asset. An attack is a threat that is carried out and, if successful, results in an unfavourable security breach or threat consequence.
The Bad Guys
To better understand cybersecurity, we need to know more about The person or group that does the attack is called an adversary or threat agent. I listed three main types of these that could be dangerous:
Undoubtedly, there are thieves or professional criminals who are interested in making a profit from the information that they can obtain through theft. For financial gain, they wish to make use of our personal information.
Activists who use the Internet, and hacking in particular, pose a new threat. These people are labelled hacktivists since they try to accomplish something with their actions. They may have an issue with who you are or what you're doing.
Nation-states can pose a threat. Political gain is the motivation, but they're also spying on one another. We've seen a number of nation-state attacks in the headlines recently.
Risks
As we can see, the risk associated with online assets is increased by attacks and vulnerabilities. Owners will make every effort to reduce such a risk, and one method of accomplishing this is by deploying defences and developing countermeasures.
Defences
We know that there are dangerous sources that will pose threats to the systems we're discussing. However, one method of dealing with both the threat source and any vulnerabilities that may exist is to deploy defences. A defence is a countermeasure that is any method used to cope with a security attack. Ideally, a countermeasure can be created to prevent a specific sort of attack from succeeding. When prevention is not possible or fails , the goal is to detect the attack and subsequently recover from its effects. A countermeasure may introduce additional vulnerabilities. In any scenario, residual vulnerabilities may exist after countermeasures are implemented. Such flaws could be used by people who want to harm the assets, putting those at risk.
Conclusion

My goal in writing this post was to explain what cybersecurity is and how it relates to information security. If we know the terms, we will have a better understanding of security and a solid foundation upon which to build.
References
- Goodreads: Computer Security - William Stallings, Lawrie Brown
- Cover photo based on: Luis Villasmil, Marek Piwnicki pictures on Unsplash
- Concrete picture: Pixabay

